|
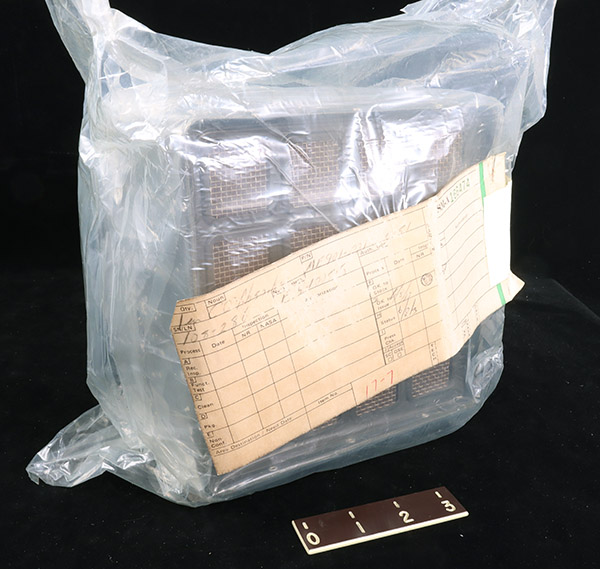
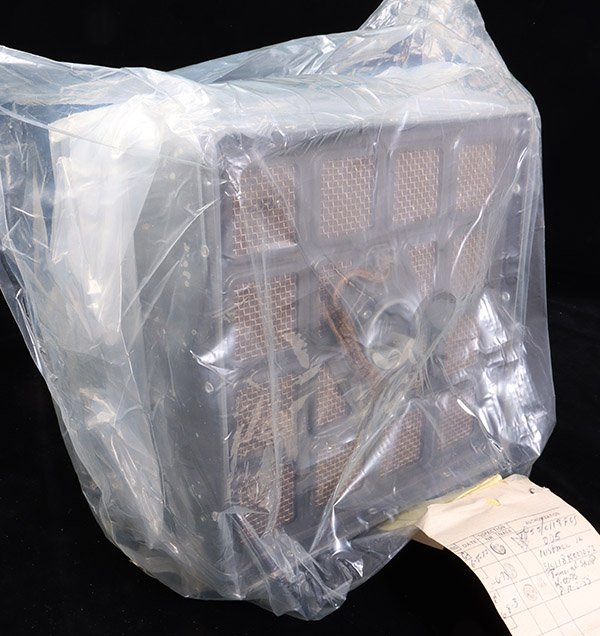
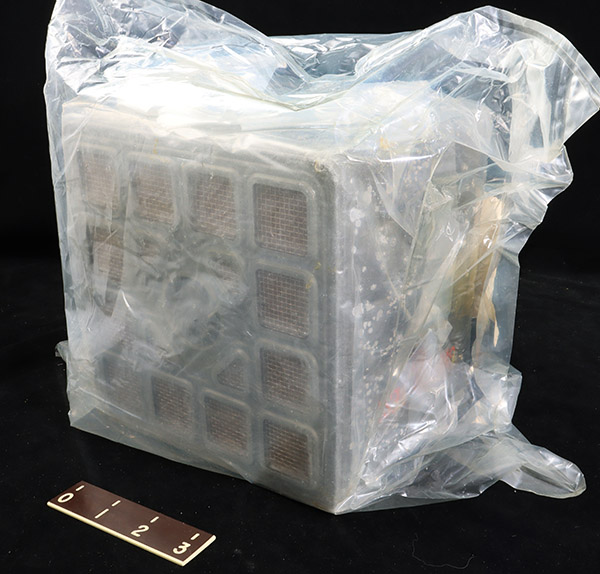
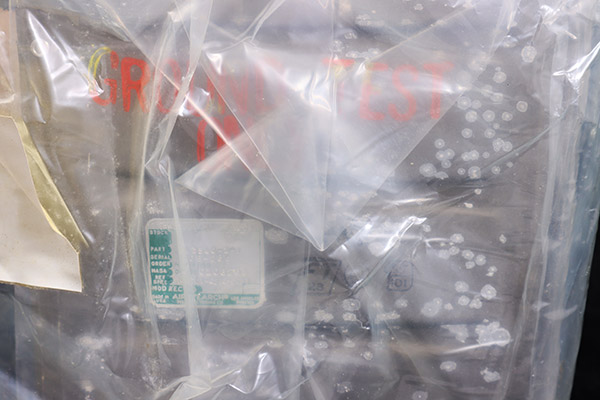
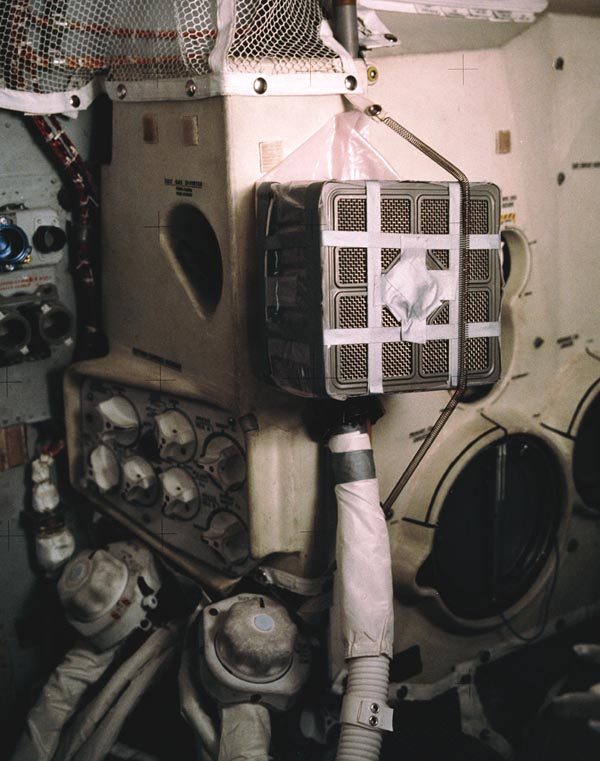
During the Apollo 13 mission the astronauts were stranded in the Lunar Module for much of the mission. Using
instructions from the ground they improvised a way to adapt the Command Module carbon dioxide absorbers for use in the Lunar Module. Otherwise the increased amount of carbon dioxide in the cabin air from
the astronauts own breathing would have killed them.
|